Three Things to Know before using Radar
Three Things to Know
before using Radar
- 01Advantages of Radar (compared to other sensors)
- 02Applications
- 03Characteristics and Applications of Each Frequency
Advantages of Radar
(compared to other sensors)
| Radar | LiDAR | Ultrasonic sensor | Vision Sensor (Camera) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weather resistance (rain, fog, dust) |
◎ | △ | △ | △ |
| Weather resistance (nighttime, backlighting) |
◎ | △ | ◎ | △ |
| Vital sensing | ◯ | × | × | × |
| Privacy | ◎ | △ | ◎ | × |
| Medium range detection (5 - 30 m) |
◎ | ◎ | × | ◯ |
| Long range detection (>30 m) |
◎ | ◯ | × | ◯ |
| Range accuracy | ◎ | ◎ | ◯ | △ |
| Speed detection | ◎ | △ | × | ◯ |
| Angle detection | ◯ | ◎ | × | ◯ |
| Size | △ | △ | ◯ | △ |
| Cost | ◯ | △ | ◎ | ◯ |
※The above table is based on S-Takaya research.
Radar can detect in adverse conditions such as rain and fog, as well as in nighttime and backlighting environments. Therefore, it is highly suitable for outdoor applications such as collision avoidance for drones and vehicles.
Also, radar is suitable for situations where privacy considerations are important. Without capturing images as visual sensors or cameras do, it can detect anomalies such as sudden illness in privacy-sensitive areas such as restrooms and bathrooms.
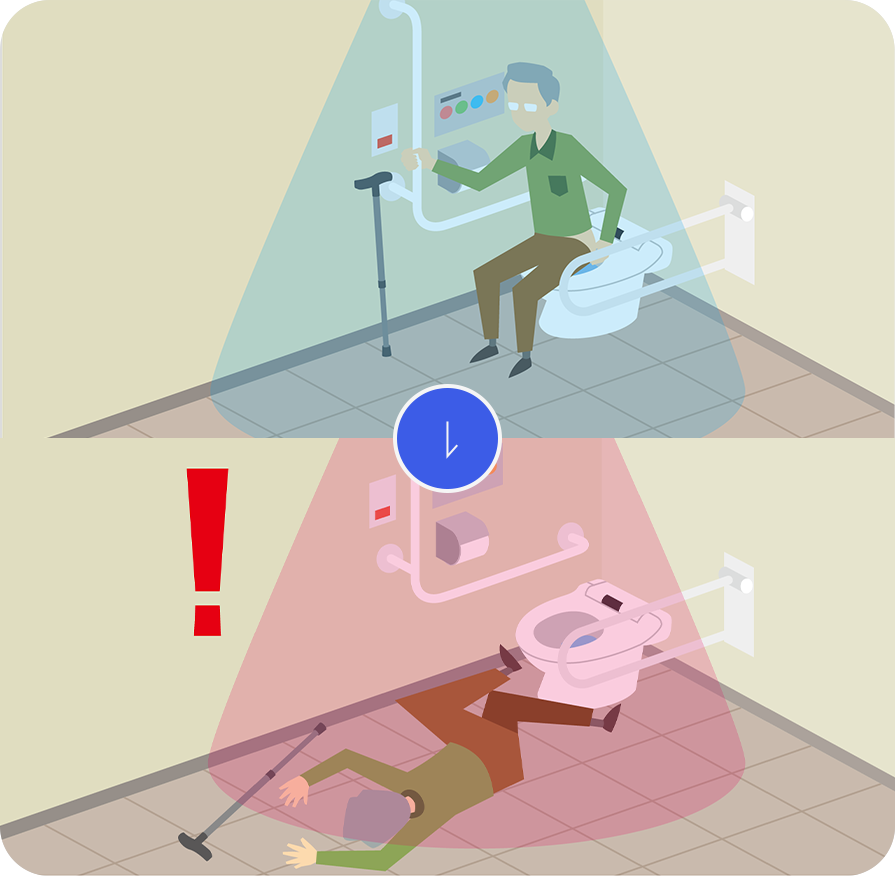
It can also be applied to detect changes in medical conditions and incidents like suffocation in infants and caregiving environments.
If radar can achieve the recognition processing that cameras and LiDAR excel at, it can gain advantages that other sensors do not have, such as weather resistance. Additionally, unlike cameras, radar does not suffer from detection issues due to lens dirt, making it maintenance-free, which is a significant benefit.
Here are some examples of radar applications.
Applications
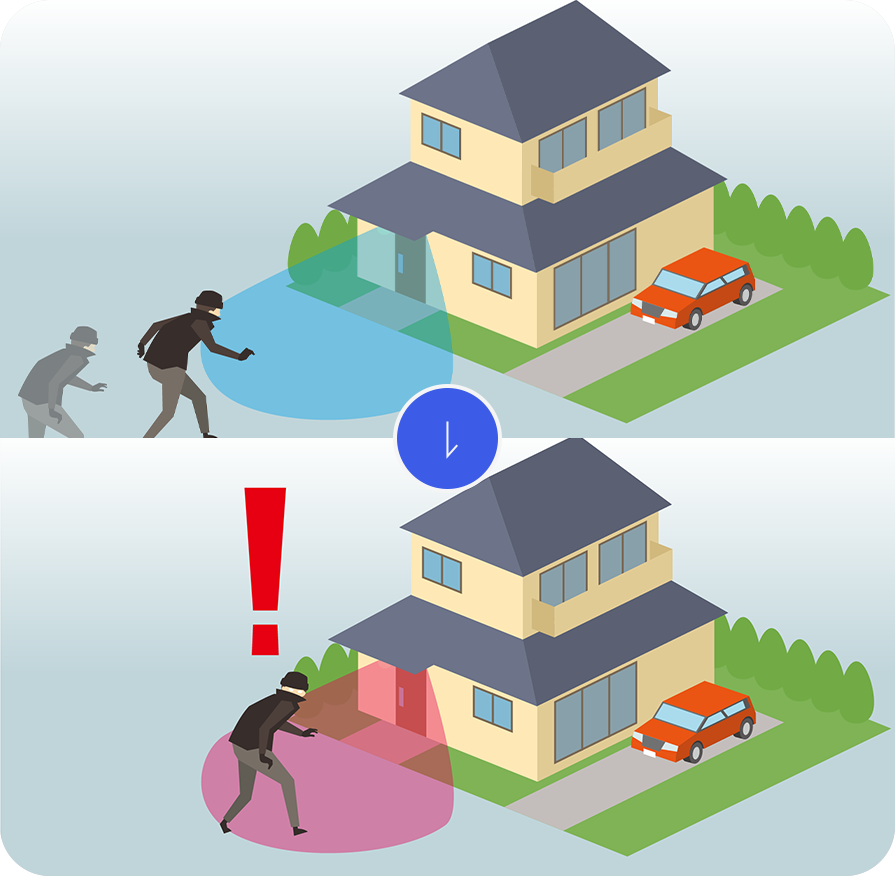
Anti-crime measure
Radar can detect intrusions by suspicious individuals into premises, determine their distance and angle, and is expected to be effective as a security measure.
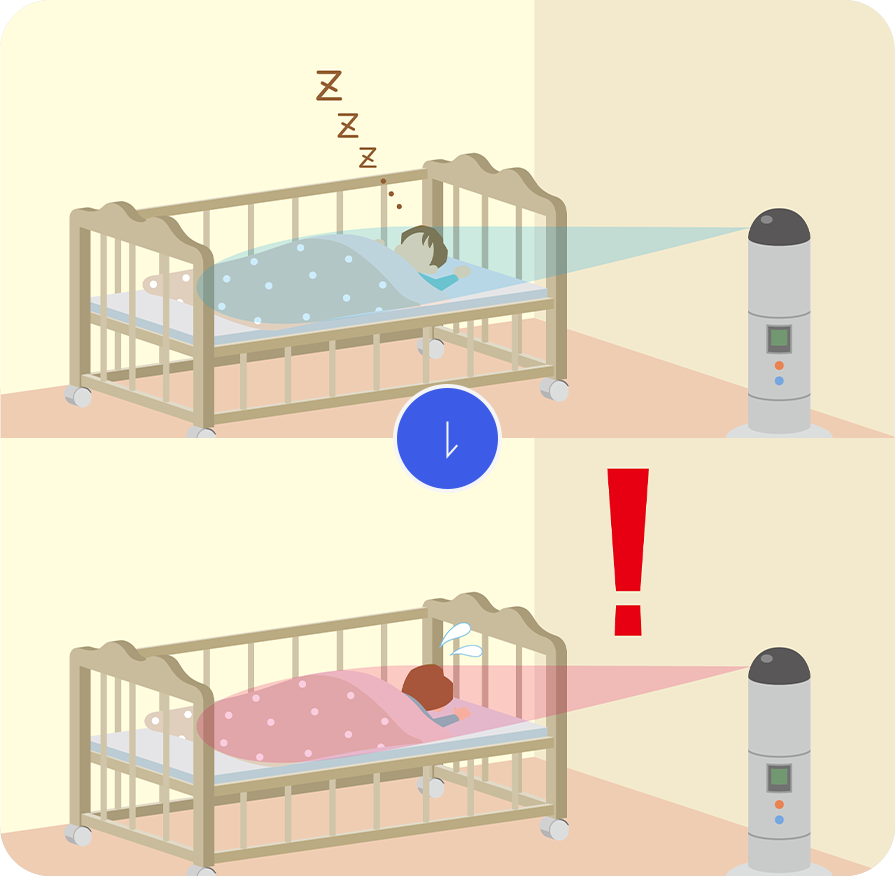
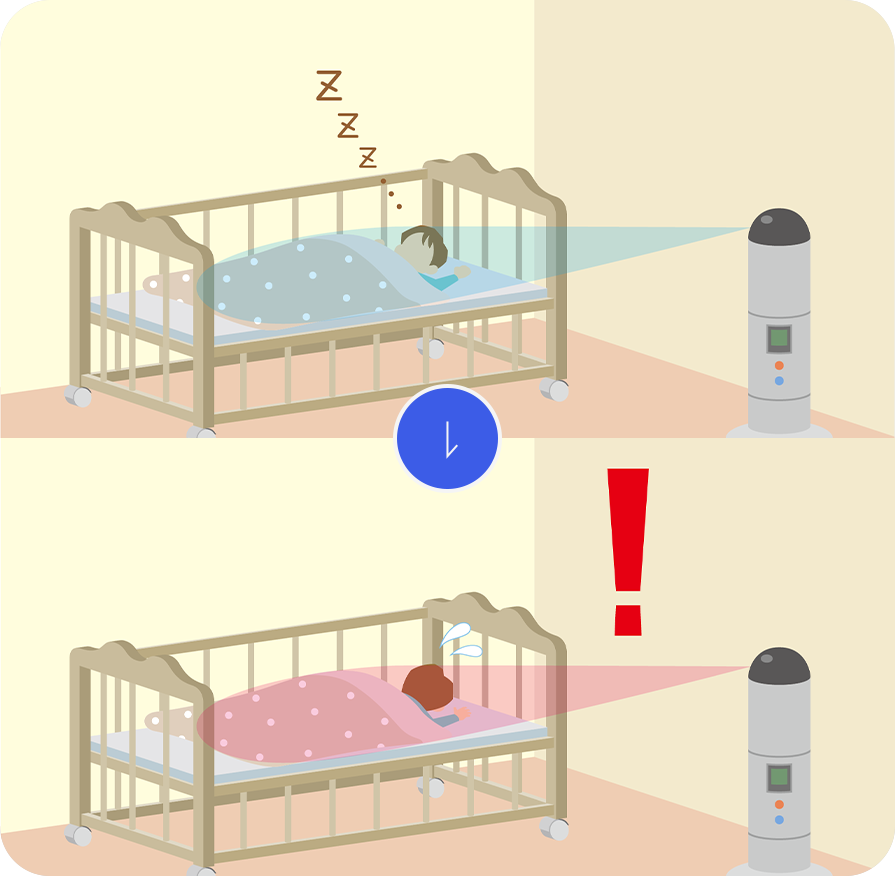
Vital sign monitoring
It can identify changes in medical condition by detecting breath and pulse on the bed, and thus, it can prevent accidents such as suffocation.
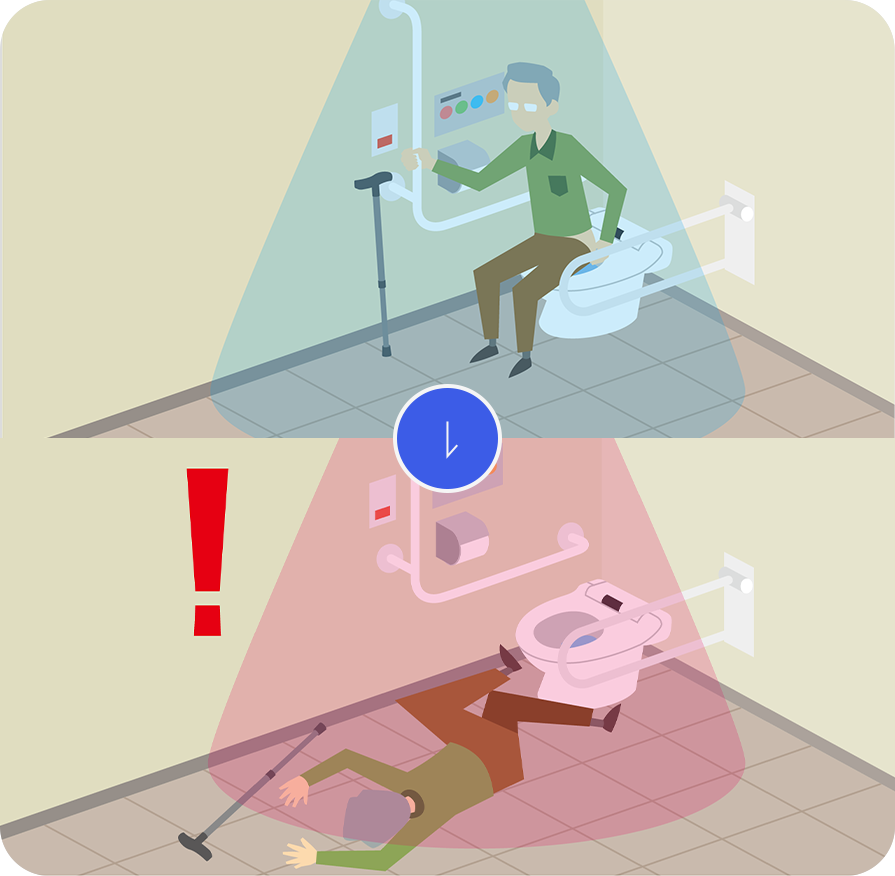
Safety detection
It can detect sudden illnesses and abnormalities while considering privacy as it is not possible to install cameras in the private places (e.g. toilet and bathroom).
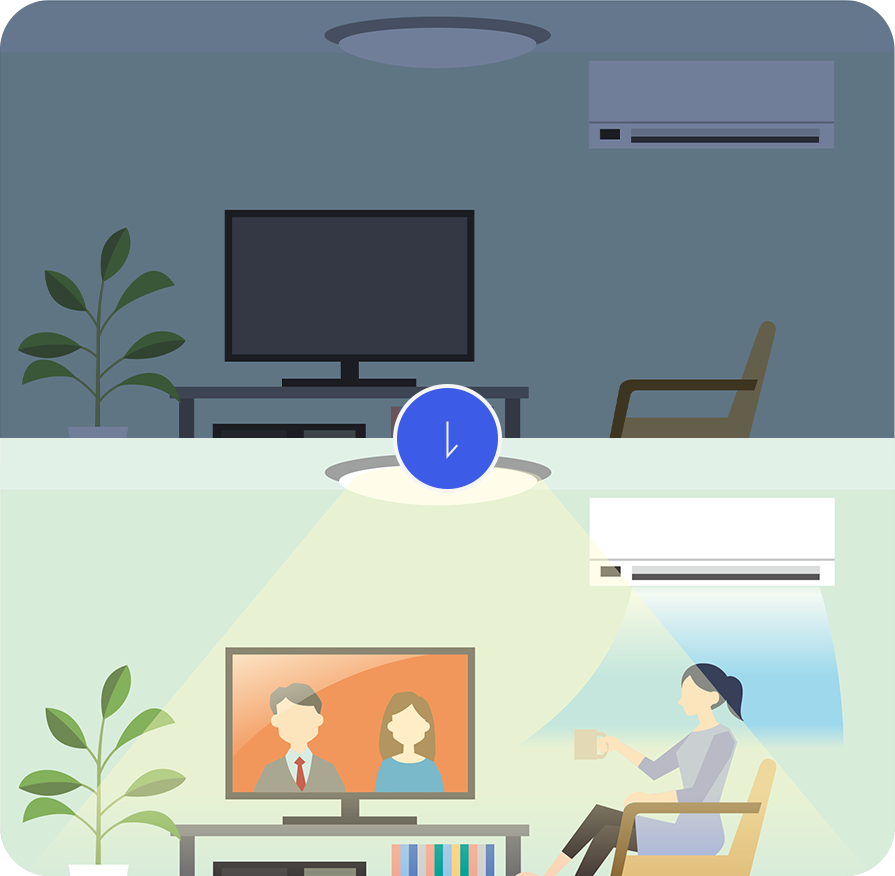

Energy-saving device
Through combination with lights and home appliances, it can be applied as energy-saving device as the radar enables automatic control of power supply via detecting human activities.
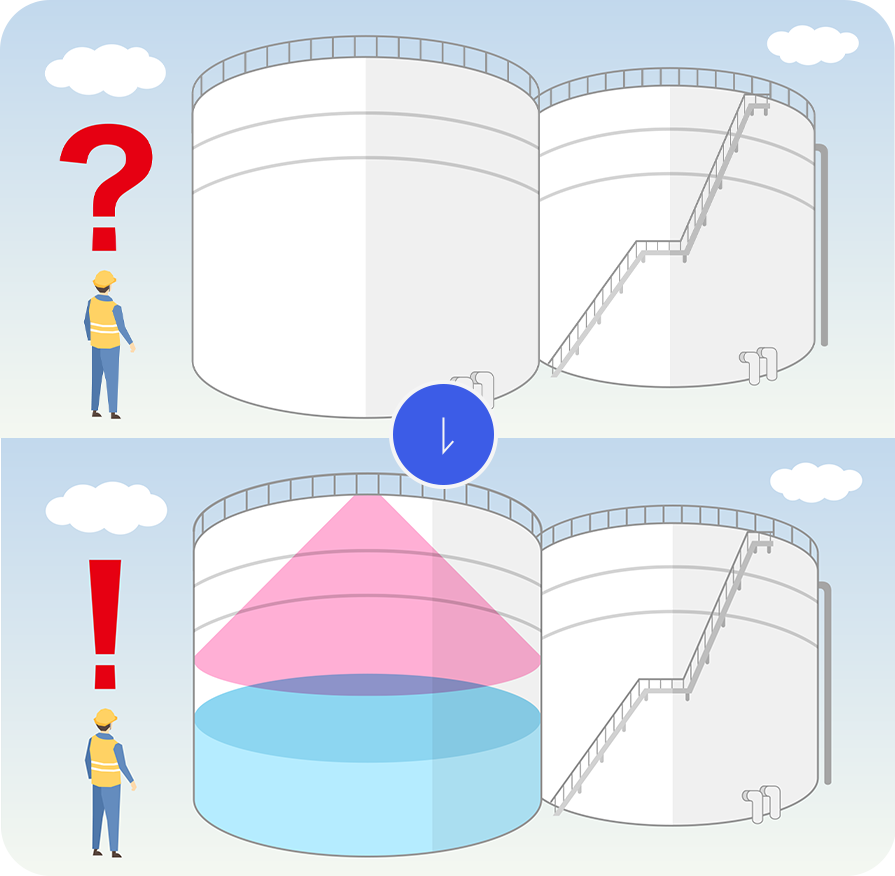
Non-contact level meter
With the characteristics of radar, it can measure the capacity inside tanks and the water level of rivers without being affected by fog or dust.
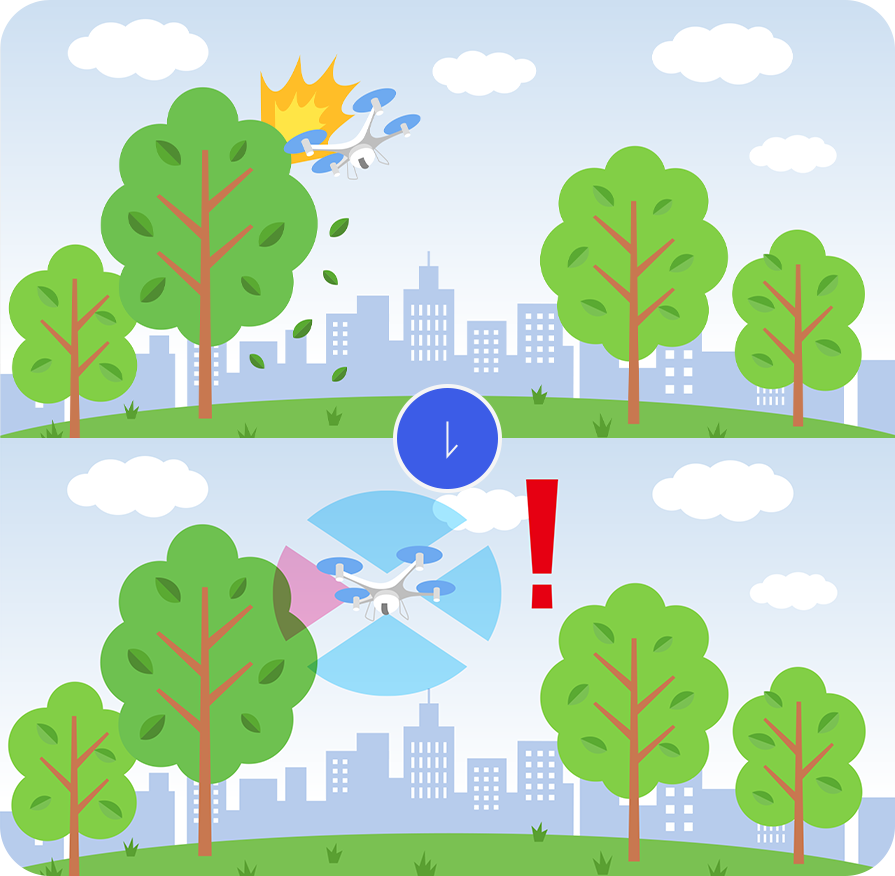
Collision avoidance for drones
Radar is expected to be used for detecting obstacles around drones and for monitoring the surroundings of drone ports.
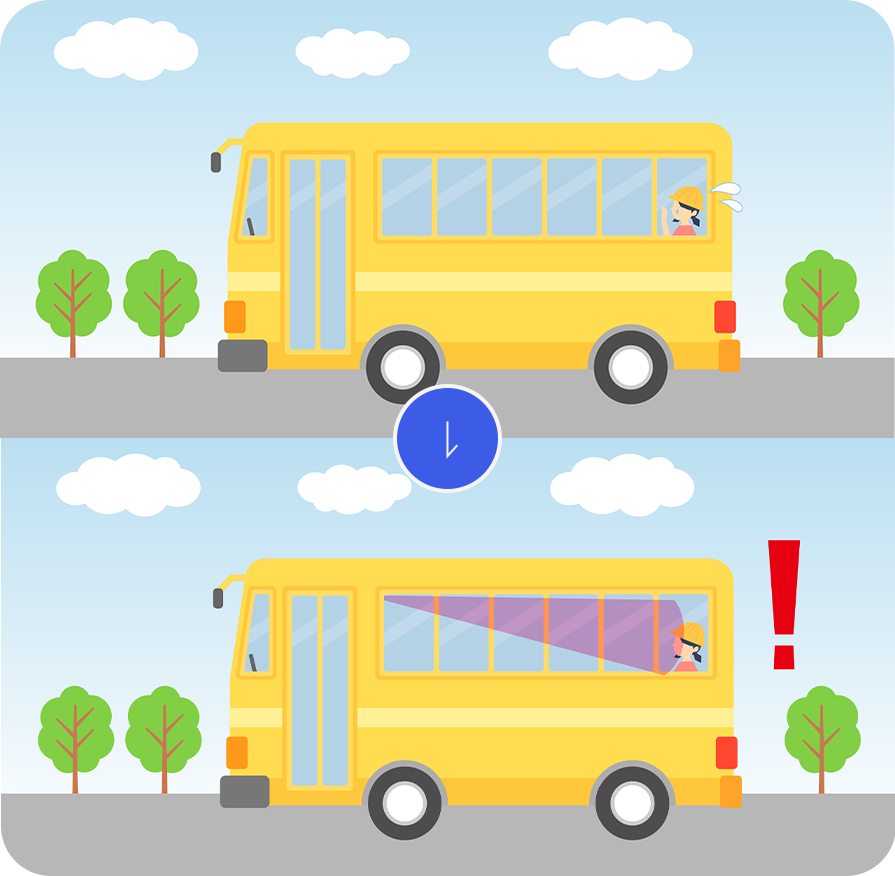
Human safety monitoring sensor
Radar is expected to be used for collision monitoring in parking lots and as a sensor for detecting people remaining in the vehicle.
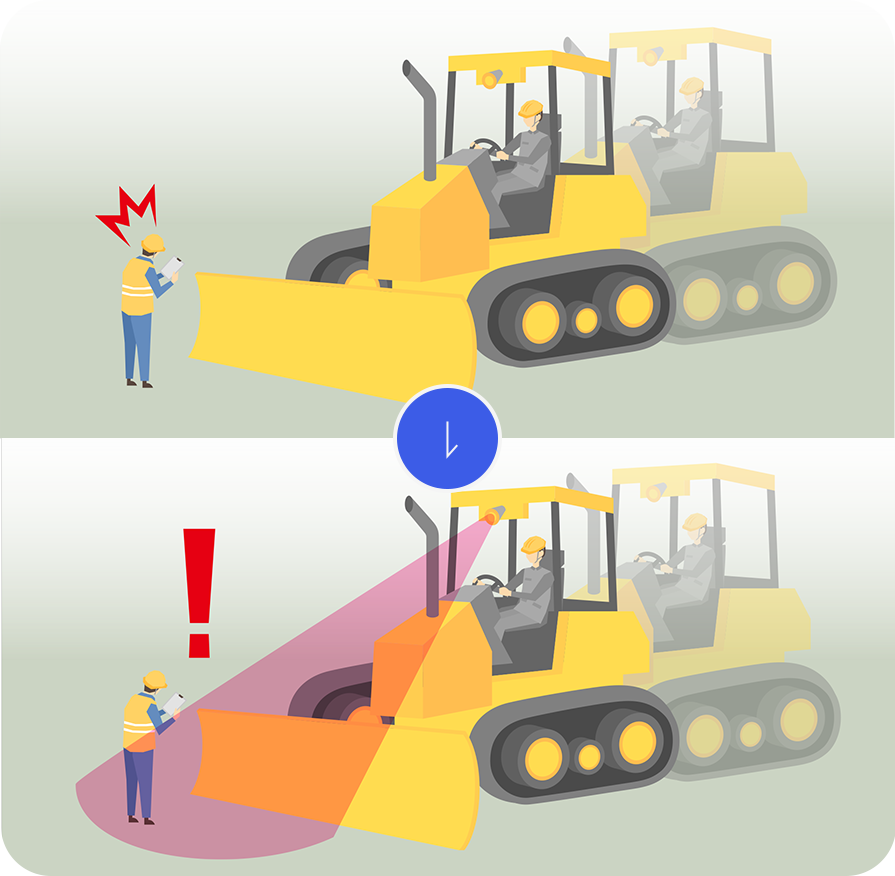
Collision prevention for construction machinery
Radar, which has strong environmental resistance, is used in construction machinery where accidents during construction are a problem. The radar is utilized as a sensor to prevent people from being caught in accidents, even in adverse weather conditions.
Characteristics and Applications of Each Frequency
Characteristics of each frequency
Each radar frequency has its own advantages and disadvantages. It is recommended that customers select the radar frequency that best suits their application.
| Advantages | Disadvantages | |
|---|---|---|
| 24GHz |
Low frequency and easy to handle
Can be used outside Japan |
Large size
Cannot detect high-speed IC products are not so many |
| 60GHz |
High distance accuracy
Small size Can be used outside Japan |
Output limitations for wide bandwidth
Many legal restrictions High difficult level required for the test Fewer IC manufacturers |
| 76/79GHz |
High distance accuracy
Small size More IC manufacturers |
Not available outside Japan (for automotive use only).
Usage restrictions in the air (e.g., drones) |
Frequencies suitable for each application
Radar has frequencies suitable for each application. The table below serves as a guideline.
| 24GHz | 60GHz | 76GHz | 79GHz | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Security | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ |
| Monitoring | ◯ | ◯ | △ | ◯ |
| Vital Sensing | ◯ | ◯ | △ | ◯ |
| Energy-Saving | △ | ◯ | △ | △ |
| Non-Contact Level Meter | △ | ◯ | △ | ◯ |
| Drones | ◯ | ◯ | × | × |
| Automotive | △ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ |
| Construction Machinery | △ | ◯ | △ | ◯ |
| Parking Lot | △ | ◯ | △ | ◯ |
| People Counting | △ | ◯ | △ | ◯ |
| Animal Detection | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ |
| Gesture Detection | × | ◯ | × | △ |